Table of Contents
Imperix controllers feature 4 clock generators, CLK0, CLK1, CLK2 and CLK3, running at 250 MHz. They provide time bases for FPGA resources such as the ADC and PWM, and subsequently trigger CPU events. In multi-device configurations, all clock generators are intrinsically synchronized within ±2 ns. Moreover, all the clock generators are reset at the same time, which implies that, if the frequency of a clock generator is a multiple of another one, they are guaranteed to stay in phase (e.g. 20kHz and 40 kHz).
The main clock CLK0 is already embedded in the CONFIG block. It is always actives and serves as the clock sources for the essential events such as generating the sampling strobe SLCK and triggering the CPU task.
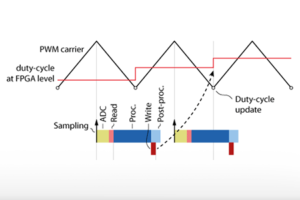
The CLK block is used to configured the optional CLK1, CLK2 and CLK3, which can be connected to PWM blocks. They support glitch-less reconfiguration during runtime as described in the variable frequency operation page.
More details on the configuration and use of the different clocks available can be found on the timing configuration for imperix controller page.
Simulink block
- The output can be connected to a PWM block input signal
>to set its switching frequency. - The input is only visible if the
variableparameter is selected. It sets the frequency of the clock during runtime.
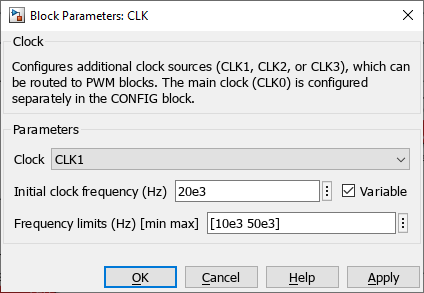
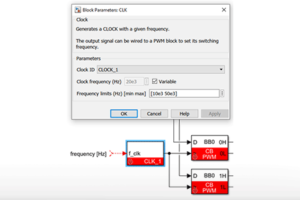
Standard parameters
- The Clock ID selects which clock generator to configure between CLK1, CLK2 and CLK3.
CLK0 is already used by the CONFIG block and cannot be instantiated in a separate clock block. - The initial clock frequency configures the frequency of the clock in Hertz (Hz). If the desired frequency is not achievable (because of the peripheral resolution of 4 ns), the clock frequency is replaced by the closest achievable frequency and a warning log message is generated in Cockpit.
This value is overwritten by the input signal value during runtime if the frequency is configured as Variable.
Advanced parameters
- The Variable checkbox enables the reconfiguration of the clock frequency during runtime using the input signal.
- The Frequency limits sets the minimal and maximal frequencies that the clock generator uses as saturation points.
PLECS block
- The output can be connected to a PWM block input signal
>to set its switching frequency. - The input is only visible if the frequency value is set as Variable and it sets the frequency of the clock during runtime.
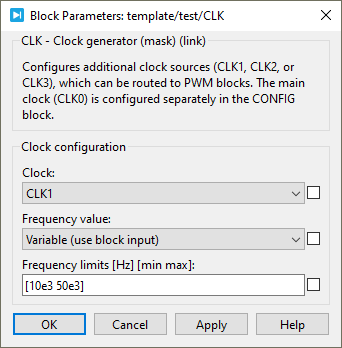
Standard parameters
- The Clock ID selects which clock generator to configure between CLK1, CLK2 and CLK3.
CLK0 is already used by the CONFIG block and cannot be instantiated in a separate clock block. - The Initial clock frequency configures the frequency of the clock in Hertz (Hz). If the desired frequency is not achievable (because of the peripheral resolution of 4 ns), the clock frequency is replaced by the closest achievable frequency and a warning log message is generated in Cockpit.
This value is overwritten by the input signal value during runtime if the frequency is configured as Variable.
Advanced parameters
- The Frequency value option can be set as Constant or Variable. Setting it as variable enables the reconfiguration of the clock frequency during runtime using the input signal.
- The Frequency limits sets the minimal and maximal frequencies that the clock generator uses as saturation points.