Table of Contents
This article explores imperix’s portfolio of programmable controllers, highlighting how each device is optimized for specific power-electronics applications.
Products presentation
All imperix controllers use a DSP + FPGA architecture that is fully programmable by the user. This shared architecture is the cornerstone of extensive hardware abstraction, which in turn authorizes excellent interoperability and compatibility across devices and generations.
From a software perspective, all programmable controllers are identical, as they can be programmed from the same Simulink/PLECS control model with only a few parameter changes. They also support the same workflow and provide the same runtime monitoring and tuning capabilities via Cockpit. At the hardware level, however, the controllers may exhibit somewhat different characteristics, notably tied to their I/O resources, each optimized explicitly for a particular use case.
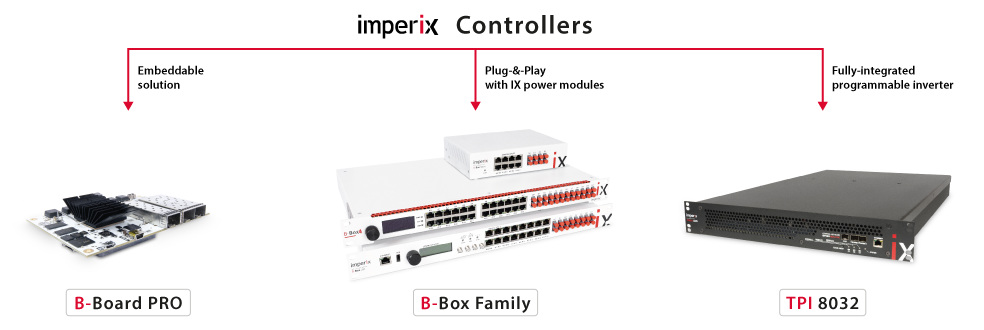
Overall, imperix offers three distinct types of programmable controllers, as shown below:
Here are the key differences between imperix controllers and general-purpose prototyping systems:
– Complimentarity among PWM signal pairs is guaranteed during 100% of the time. No 1:1 state can ever happen, including during boot time, during FPGA flashing, during power supply fault, etc. Most competing solutions produce potentially destructive signals during these brief but special conditions.
– Cockpit offer a simple enable/disable mechanism for PWM outputs. This is key to distinghuish the starting/stopping of the code from that of the application (start/stop of the whole power converter). The implementation of protections does also depend from that mechanism.
– Protections are fully independent from the user application (including inside the FPGA). This guarantees that any mistake or bug at the application level can never interfere with safety.
– Synchronous sampling is guaranteed across all channels (and all units accross the control network). Specifications are guaranteed accordingly. Sampling is also synchronized with modulation by default, with multiple advanced options available.
– Low-latency and deterministic timings are 100% guaranteed. Sampling to CPU, and CPU to modulators update is generally below 200ns (except for complex applications). This performance level is simply unachievable over PCIe (i.e. with all systems based on the x86 architecture).
– There is no pipelining during data aquisition or transfers. Acquisition, control and modulation can be executed within one sampling period, even at the maximum control rate. Hard real-time execution is guaranteed. Over-run is simply impossible (software fault).
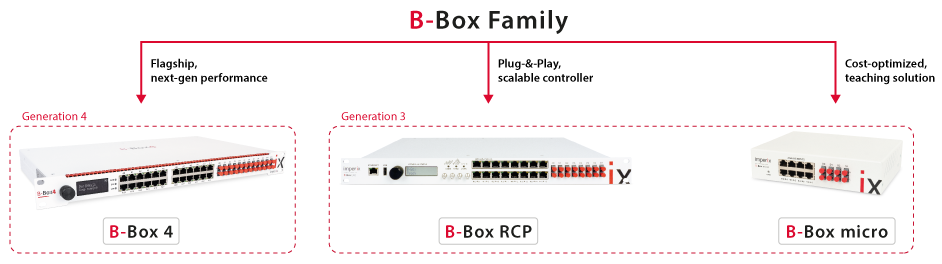
B-Box family
The B-Box family comprises devices optimized for laboratory applications, where performance and flexibility are the main priorities. B-Box controllers are plug-&-play with imperix power modules (example) but are also flexible enough to be easily used with custom power hardware (e.g. TN107). The differences between B-Box controllers are summarized below. Details specific to hardware protections are provided in PN257.
B-Board PRO
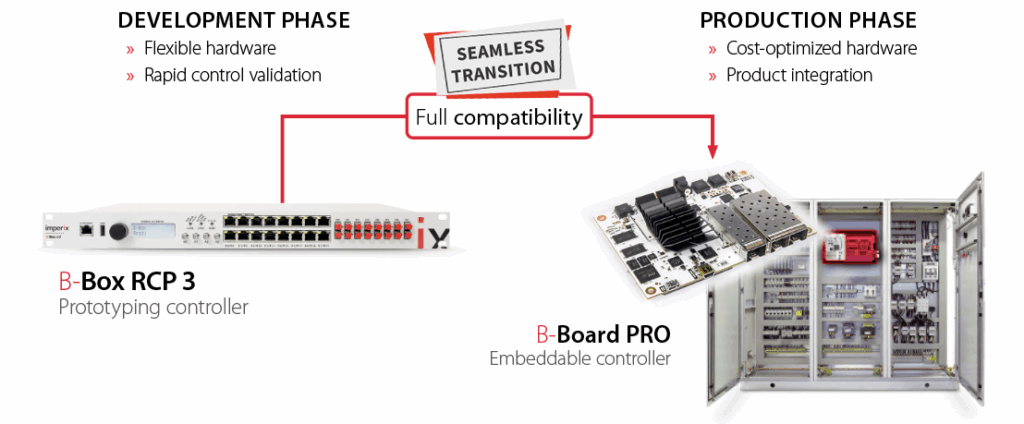
The B-Board PRO is the control board present in the B-Box RCP and B-Box micro. It is also available as a standalone control board. Its typical applications include industrial use or research, where the programmable controller must be embedded directly in the power converter. In such a case, the main benefit of using B-Board PRO lies in its ability to facilitate the transition between the development and production phases, thanks to immediate portability from the B-Box RCP. More information can be found on its product page.
TPI 8032
The TPI 8032 is the only imperix product that combines the power and control stages into a single unit. Standing for Three-Phase Inverter, the TPI 8032 is a fully programmable inverter optimized for maximum flexibility on the software side, but in experiments where the topology remains constant. Typical applications include grid-connected inverters and the emulation of DERs in lab-scale microgrid applications. More information on the TPI 8032 can be found on its product page.
| B-Box controllers | B-Board PRO | TPI 8032 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Application target | Modular power electronic systems | Integration within custom converters | Easy-to-use programmable inverter |
| Plug & play with modules and sensors | YES | NO | YES, but only sensors: 4x analog inputs (RJ45) |
| Processing | B-Box 4: 4×1.5GHz + 504K FPGA Gen. 3: 2×1.0GHz + 125K FPGA | 2×1.0GHz + 125K FPGA | 2×1.0GHz + 125K FPGA |
| Analog I/Os | RJ45 for analog inputs | On high-density connectors (bottom side) | 4x analog inputs on RJ45 |
| Digital I/Os | Optical fibers for PWMs VHDCI connectors for other digital I/Os | On high-density connectors (bottom side) | 8x GPIO as 5/12V electrical signals. |
| Software environments | ACG SDK or CPP SDK Free FPGA programming | ACG SDK or CPP SDK Free FPGA programming | ACG SDK or CPP SDK Free FPGA programming |
| SW-independent protections | YES | NO | YES (not configurable) |
| Product datasheet | B-Box 4 B-Box 3 (RCP) B-Box micro | B-Board PRO | TPI8032 |
B-Box devices
Within the B-Box family, imperix controllers share the same I/O interfaces: RJ45 connectors for analog inputs and plastic optical fibers (POF) for PWM outputs. Cross-compatible digital I/Os are also available on the rear side of the devices in electrical form.
On the other hand, the specificities of each programmable controller offer freedom of choice regarding:
- I/O count and related performance. The bandwidth and sampling rate of analog inputs, as well as the PWM resolution of digital outputs, differ significantly across devices.
- Computing performance. The B-Box 4 embeds a significantly more powerful processing system.
- Oscilloscoping capabilities. The B-Box 4 supports the so-called oversampling technology.
- Networking options. The B-Boxes 4 and 3 can be stacked for high-performance I/O extension, unlike the B-Box micro.
This results in the following product positioning:
- B-Box 4: Flagship controller with the most extensive set of capabilities and the highest performance. Commercialized since 2026.
- B-Box RCP 3: High-performance controller with full support for networked control and direct portability to B-Board PRO. Commercialized since 2019.
- B-Box micro: Cost-optimized, teaching-oriented system with limited I/Os. Networked control is, however, not supported.
I/O specifications
| B-Box 4 | B-Box 3 | B-Box micro | |
|---|---|---|---|
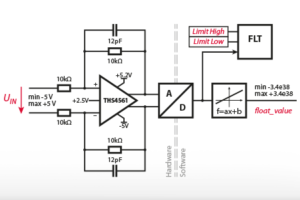
| Analog inputs | 24x RJ45 ports – Resolution: 16-bit – Simult. Fs: 20Msps – Bandwidth: 2.7MHz – Impedance: 5kΩ1 – Auto-ID: YES – Pre-amp gain: 1x – LPF: digital (precision ++) – Oversampling: YES | 16x RJ45 ports – Resolution: 16-bit – Simult. Fs: 0.5Msps – Bandwidth: 400kHz – Impedance: 3kΩ/100Ω – Auto-ID: NO – Pre-amp gain: 1x,2x,4x,8x – LPF: analog – Oversampling: NO | 8x RJ45 ports – Resolution: 16-bit – Simult. Fs: 2Msps – Bandwidth: 1.3MHz – Impedance: 20kΩ – Auto-ID: NO – Pre-amp gain: 2x – LPF: NO – Oversampling: NO |
| PWM outputs | 48x fiber/VHDCI outputs – 24x optic./elec. + 24x elec. – 250ps resolution – Oversampling: YES | 32x fiber/VHDCI outputs – 16x optic./elec. + 16x elec. – 4ns resolution – Oversampling: NO | 8x fiber outputs – 8x optical only – 4ns resolution – Oversampling: NO |
| Analog outputs | 24x RJ45 ports – Resolution: 12-bit – Update rate: 500 ksps – Shared with inputs | 4x SMA ports – Resolution: 16-bit – Update rate: 50 ksps spaceholder | Unavailable spaceholder spaceholder spaceholder |
| GPO | 48x fiber/VHDCI outputs – 24x optic./elec. + 24x elec. – Logic level: 3.3V/5V | 16x VHDCI outputs – Logic level: 3.3V/5V | 8x PCB header outputs – Logic level: 5V |
| GPI | 24x VHDCI inputs – Logic level: 3.3V/5V | 16x VHDCI inputs – Logic level: 3.3V/5V | 8x PCB header inputs – Logic level: 5V |
| USR | 36x VHDCI pins – Logic level: 3.3V | 36x VHDCI pins – Logic level: 3.3V | 36x VHDCI pins – Logic level: 3.3V |
| Product datasheet | B-Box 4 | B-Box 3 | B-Box micro |
1 Low-impedance adapter available for purchase
Computational capability
Computational capability differs only across generations. While Generation 3 controllers are powerful enough for most typical applications, with achievable maximum CPU control frequencies in the range of 250 kHz, the B-Box 4 is considerably more powerful and can run 4x more complex code at a given control frequency.
| Generation 4 | Generation 3 | |
|---|---|---|
| SoC architecture | Zynq Ultrascale+ | Zynq 7000 |
| Processing system | – 4x 1.5GHz AMD Cortex A53 -3 – 8GB DDR4 | – 2x 1.0GHz AMD Cortex A9 -3 – 1GB DDR3 |
| FPGA | Kintex US+ 504K – 350K programmable logic cells | Kintex 7 125K – 62K programmable logic cells |
| Product datasheet | B-Box 4 | B-Box RCP B-Box micro |
Supported communication protocols
Each controller supports various communication protocols. The more research-oriented devices (B-Box 4 and B-Box RCP) support many more protocols than the teaching-oriented device (B-Box micro).
| B-Box 4 | B-Box 3 | B-Box micro | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ethernet-based | 1x Ethernet port – UDP/IP – OPC-UA – Modbus TCP | 1x Ethernet port – UDP/IP – OPC-UA spaceholder | 1x Ethernet port – UDP/IP – OPC-UA spaceholder |
| High-performance | 4x QSFP+ 40Gbit/s – RealSync – Aurora – Custom protocol | 3x SFP+ 10Gbit/s – RealSync – Aurora – Custom protocol | Unavailable spaceholder spaceholder spaceholder |
| CANBUS | 2x CANBUS ports – CAN FD – CAN 2.0A – CAN 2.0B | 1x CANBUS ports – CAN 2.0A – CAN 2.0B spaceholder | Unavailable spaceholder spaceholder |
| Serial communication | 2x serial ports – RS422/RS485 – BISS-C/SSI/Endat 2.0 | Unavailable spaceholder spaceholder spaceholder spaceholder | Unavailable spaceholder spaceholder spaceholder spaceholder |
| Product datasheet | B-Box 4 | B-Box 3 | B-Box micro |
Software-independent protections
The software-independent protections available on most imperix controllers have slightly different characteristics, which are summarized in the table below. Further details are given in PN257.
| B-Box 4 | B-Box 3 | B-Box micro | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Implementation | Protected FPGA firmware | Hardware comparators | Protected FPGA firmware |
| Scaling | Identified sensor: true value Third-party sensor: ADC value | ADC value | ADC value |
| Response speed | Ultra: <800ns Fast: 1.6µs | Fast: 1.6µs | Fast: 1.5µs |
| Configuration | In Cockpit | using the front panel1 | in Cockpit |
| Product datasheet | B-Box 4 | B-Box 3 | B-Box micro |
1 Saving/restoring the protection configuration requires a USB key on the B-Box RCP3.0, as it’s entirely independent of Cockpit.
Application-based selection guide
Every imperix controller can run most control algorithms with excellent closed-loop performance. Nonetheless, imperix’s controller portfolio aims to provide solutions optimized for each use case.
When to select a B-Box controller
When comparing imperix products, the primary motivations for choosing a B-Box controller is the versatility offered by its modular design and plug-and-play compatibility with imperix power modules. This enables changing the controlled topology in a couple of minutes by simply rewiring the power stage and changing the I/O mapping. The selection of the specific B-Box type depends on user requirements:
Selecting the B-Box 4
The B-Box 4 is imperix’s flagship controller. Apart from offering the highest number of I/Os, it also provides access to oversampled ADC and PWM data, enabling their scoping directly in Cockpit. This makes it the first-choice controller for easily researching and debugging high-performance applications. Examples where this would prove particularly useful include:
Selecting the B-Box RCP
As the previous flagship of the imperix controller portfolio, the B-Box RCP is a highly capable device that performs well across a wide range of applications. Its only limitations are the comparatively lower processing power and the lack of oversampling. Usage examples are:
Selecting the B-box micro
The B-Box micro is as computationally capable as the B-Box RCP but has fewer I/Os (and a lower cost!). This makes it the ideal controller for teaching various concepts in power electronics that do not require a large number of I/Os. Usage examples are:
When to select the TPI8032
The TPI8032 is the preferred controller/converter for lab-scale experiments on microgrids and distributed generation, as it combines the programmability of the B-Board PRO with an all-in-one integrated two-level three-phase inverter with grid connection filters included. This makes it the perfect solution when flexibility in topology is not required, but flexibility in control behavior is. The inverter can be programmed in various ways, and can also be paralleled for increased power. Usage examples are:
When to select the B-Board PRO
The B-Board PRO is specifically designed to be embedded into a pre-implemented or custom-designed power stage. It optimizes for better packaging at the expense of the flexibility and plug-&-play capability offered by B-Box controllers. Usage examples are: