This article describes how to use the Rolling plot module of imperix Cockpit to interact with the user code running on imperix power converter controllers, namely the B-Box 4, B-Box RCP, B-Board PRO, the B-Box Micro, and the Programmable Inverter. This page provides a detailed explanation of all of the module’s features.
For new users, it is recommended to read the following articles beforehand to get started with the imperix software development kit (SDK) and imperix Cockpit monitoring software:
Rolling Plot basics
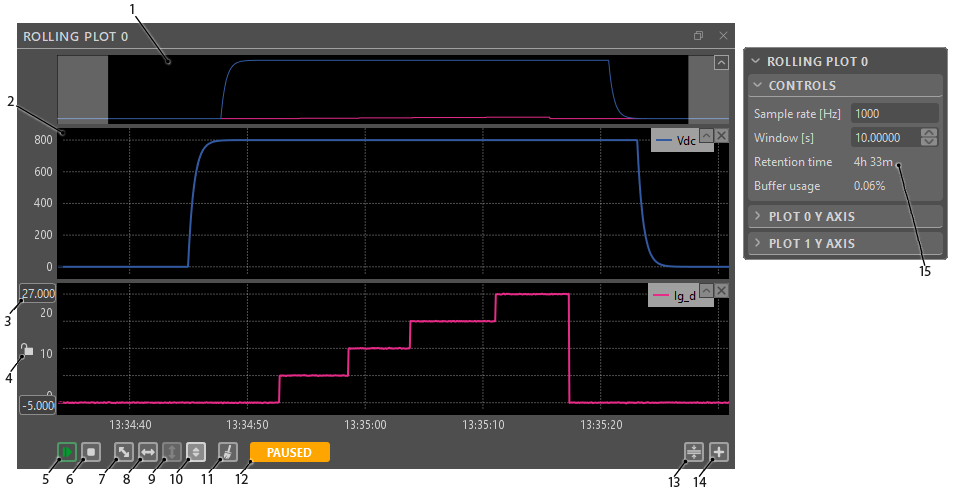
The rolling plot module allows for more long-term monitoring of the selected variables. A typical use case is monitoring the long-term evolution of the converter state in order to keep an eye on critical variables.
The sampling frequency of the Rolling plot can range from 10Hz up to the CPU control task frequency. The maximal amount of the recorded data depends on this value and the number of acquired variables. Once the allocated memory buffer fills up, the oldest acquired points will be deleted.
Rolling Plot interface
Rolling Plot tips and tricks
- To add multiple variables to a plot, open the user variable section of the project pane. Keep the ctrl key pressed and click on the desired variables to select them. Alternatively, click on the first variable to select, keep the Shift key pressed, and click on the last variable to select. These selected variables can then be dragged and dropped into a plot all at once.
- To zoom in and out along the horizontal axis, place the mouse cursor where to zoom. Then, use the mouse wheel to zoom in or out around the mouse cursor.
- To zoom in and out along the vertical axis, place the mouse cursor where to zoom. Then, press the ctrl key and use the mouse wheel to zoom in or out around the mouse cursor.
- To zoom on a specific area, click and drag to draw a blue rectangle over the zoom area.
- To achieve a horizontal autoscale, right-click and drag horizontally. A light grey horizontal strip will appear. Release the mouse button to perform the horizontal autoscale.
- To achieve a vertical autoscale, right-click and drag vertically. A light grey vertical strip will appear. Release the mouse button to perform the vertical autoscale.
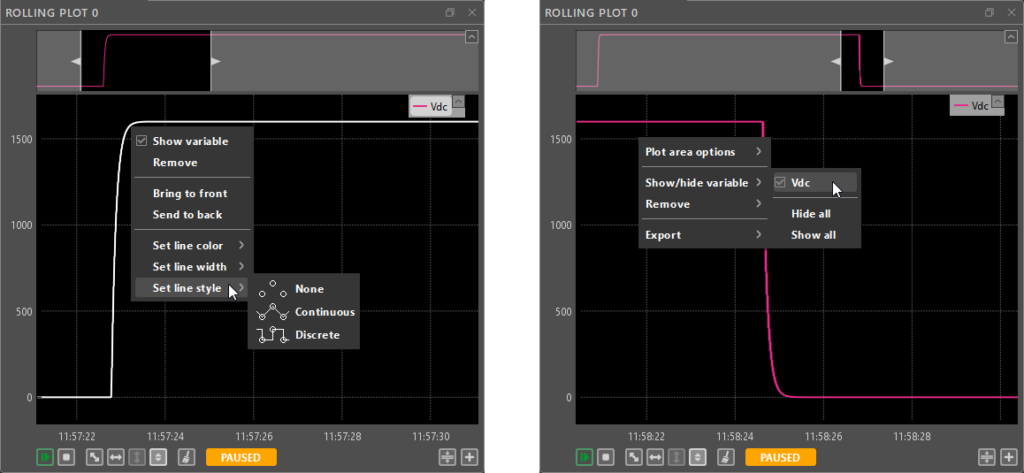
- Many of the Rolling Plot functionalities can also be accessed through context menus by right-clicking on a plotted variable or on the empty space in the plots.