DO-PWM – Direct output PWM
The Direct output PWM block sets PWM output(s) directly to ‘0’ or ‘1’. This technique is typically used for Model Predictive Control (TN162) or Direct…
The Direct output PWM block sets PWM output(s) directly to ‘0’ or ‘1’. This technique is typically used for Model Predictive Control (TN162) or Direct…

The Carrier-based PWM block generates PWM signals based on one of the 4 carrier shape illustrated below: triangle, sawtooth, inverted triangle, inverted sawtooth. When using…

The Pulse Width Modulators (PWM) share the dead-time generation and the activate/deactivate features, configured through the output mode, deadtime, and activate parameters. The said PWM…

The angle decoder (DEC) block decodes quadrature-encoded signals produced by incremental encoders for motor drive applications. The B-Box RCP and B-Board PRO provide decoder inputs…

This page is based on SDK 2025.2. Imperix controllers feature 4 clock generators, CLK0, CLK1, CLK2 and CLK3, running at 250 MHz. They provide time bases…

This page is based on SDK 2025.2. The CONFIG block is mandatory and serves to configure the main clock CLK0, the sampling clock SCLK and…
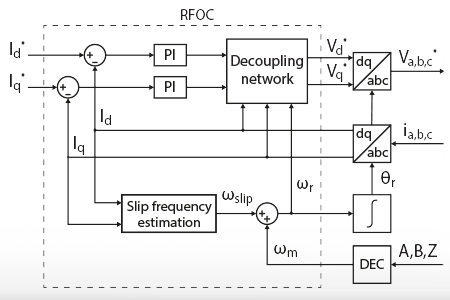
This note covers the rotor field-oriented control of an induction machine and its implementation on a user-configurable voltage-source inverter.
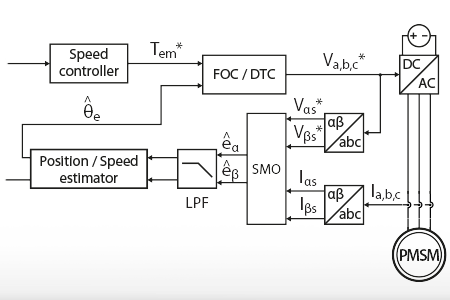
This technical note addresses the sensorless control of motor drives using a back-EMF sliding-mode observer. The technique allows speed and position estimation of a Permanent…
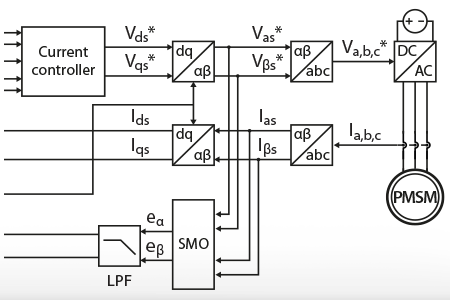
This note covers the I-f startup method for speed sensorless motor control and its implementation on a programmable power converter prototype.
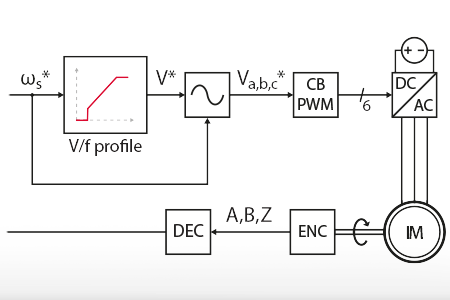
This note covers the V/f control of an induction machine and its implementation on a programmable drive inverter.
End of content
End of content