ANN-based control of a three-phase inverter
Conventional model-based control in power electronics relies heavily on deriving precise mathematical models of the physical system. In contrast, data-driven control shifts this paradigm by…
These notes present solutions for the implementation of control software, with practical, imperix-related aspects in mind. They mostly focus on one specific subsystem and may link to other technical notes if needed. Technical notes are application-independent.
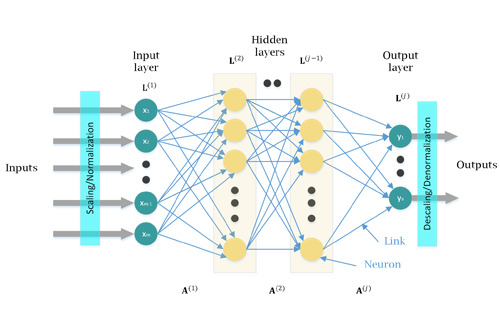
Conventional model-based control in power electronics relies heavily on deriving precise mathematical models of the physical system. In contrast, data-driven control shifts this paradigm by…
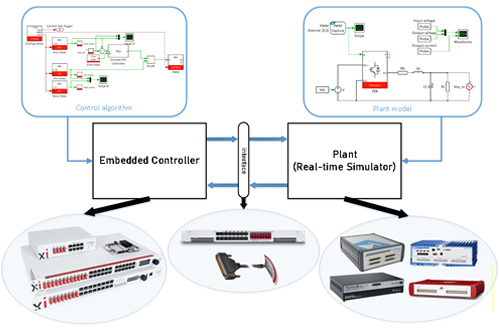
This technical note introduces the basic principles of HIL simulation and provides practical considerations for the implementation of a controller-HIL setup using the imperix B‑Board…

This note describes the control of an adapted Siemens SINAMICS S120 active line module using the imperix B-Board PRO embedded control platform. With its low…

This guide provides an overview of key points to consider when testing power converters in a laboratory environment, covering personnel safety, equipment protection, and the…
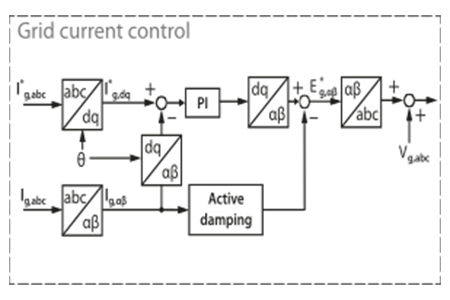
Switching ripple filters are commonly added to grid-connected voltage source converters (VSCs) to filter out undesirable switching harmonics from the VSC’s output voltage. LCL filters…

What is islanding detection? Islanding occurs when part of a power network, disconnected from the main grid, is solely powered by some Distributed Energy Resources…

This technical note provides an overview of Active Power Filters (APFs) designed for harmonic mitigation and specifically targeting three-phase grid-connected inverters. The note begins by…
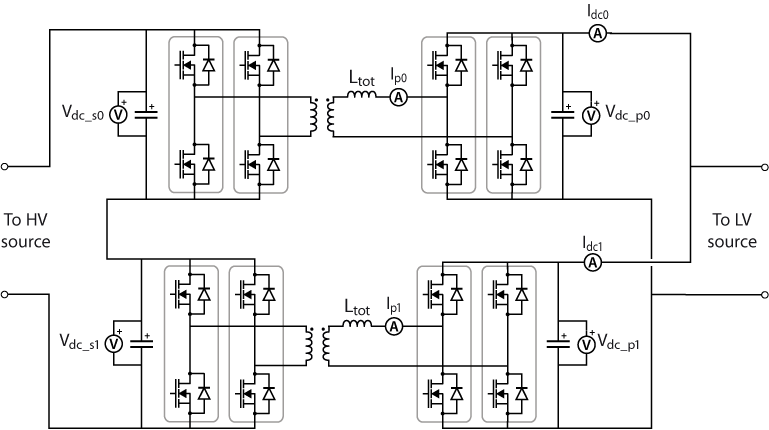
The DC transmission systems are widely used in DC grids, rail transit systems, and electric vehicle charging systems. In these applications, the DC supply can…
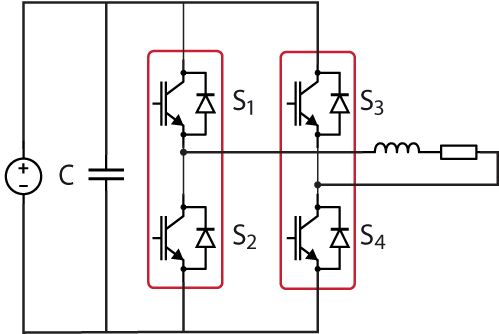
This technical note introduces the working principles of a single phase inverter. It presents a simple technique to generate an alternating current in an open-loop…
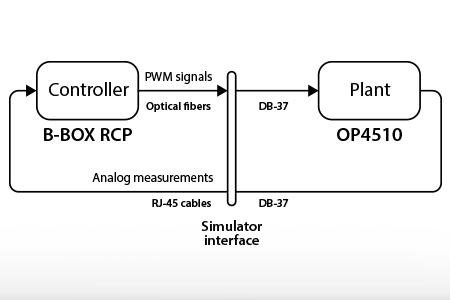
This page presents a first HIL example to get started with a B-Box RCP and an OPAL-RT OP4510. Although validated with an OP4510, the provided…
End of content
End of content