I-f startup method for sensorless PMSM control
This note covers the I-f startup method for speed sensorless motor control and its implementation on a programmable power converter prototype.
These notes present solutions for the implementation of control software, with practical, imperix-related aspects in mind. They mostly focus on one specific subsystem and may link to other technical notes if needed. Technical notes are application-independent.
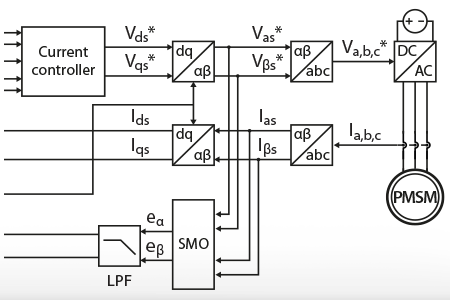
This note covers the I-f startup method for speed sensorless motor control and its implementation on a programmable power converter prototype.
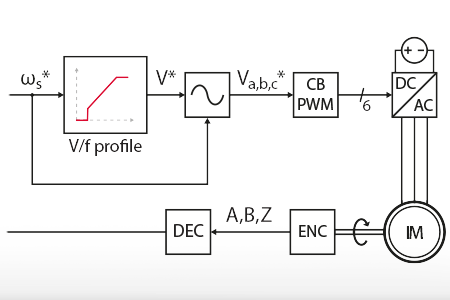
This note covers the V/f control of an induction machine and its implementation on a programmable drive inverter.
This note introduces a conventional control for Modular Multilevel Converters (MMC). The converter is used in a DC/AC inverter configuration and is connected to the three phase grid.

This example generates three phase alternating currents from a voltage source inverter in an open loop manner. It can be used in a grid-forming application.
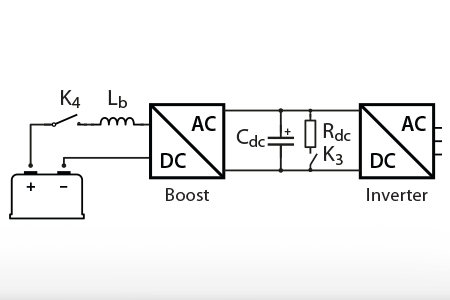
In voltage source converters, pre-charging the inverter DC bus is required before connecting it to external voltage sources, so that to avoid inrush currents that may be destructive.
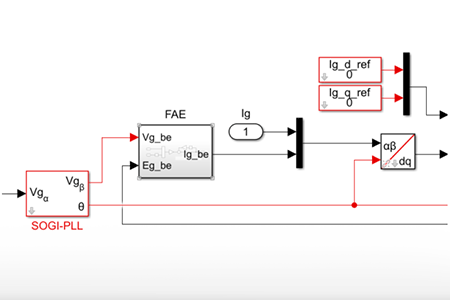
Fictive axis emulation is a vector control technique that is mostly used in single-phase inverter applications, where the second axis β of a rotating reference…
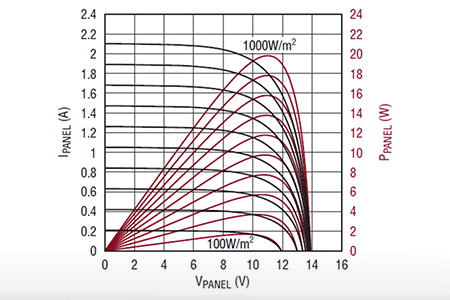
Some power sources, like solar panels, present power characteristics that strongly depend on the operating conditions. In such cases, Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) is often applied to maximize the extracted power.
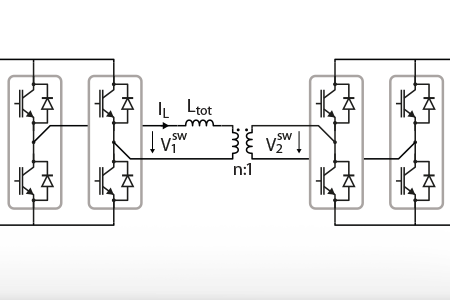
This note presents several modulation techniques to operate a Dual Active Bridge (DAB) converter. First, the topology and the theoretical aspects of the Dual Active…
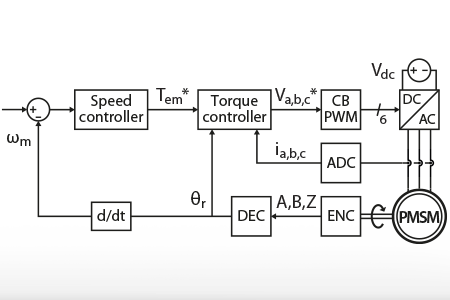
This technical note explains how to implement speed control for an electric motor. First, the note introduces the general operating principles of motor speed control,…
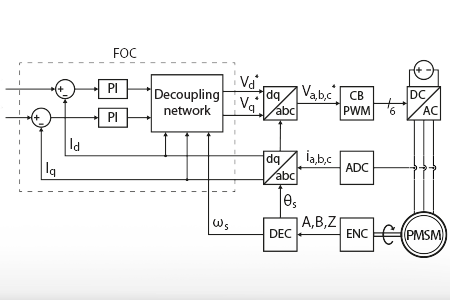
The Field-Oriented Control (FOC) method is a motor control strategy that orients the stator current vector in a rotating reference frame of the machine.
End of content
End of content