Introduction to Model Predictive Control
This article aims to explore the Model Predictive Control (MPC) methodology in-depth, focusing on its operational principles, classification, and comparative analysis with conventional PID-based control….
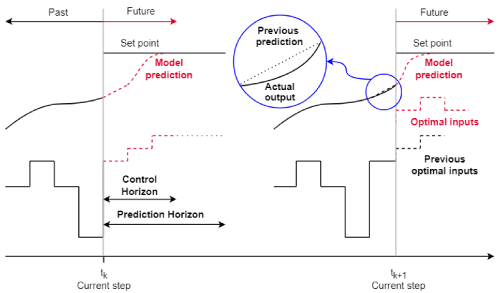
This article aims to explore the Model Predictive Control (MPC) methodology in-depth, focusing on its operational principles, classification, and comparative analysis with conventional PID-based control….
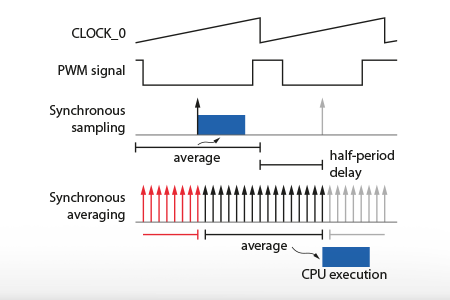
Synchronous averaging is a measurement processing method that computes the average value of an analog signal over one full switching period. In contrast, synchronous sampling…
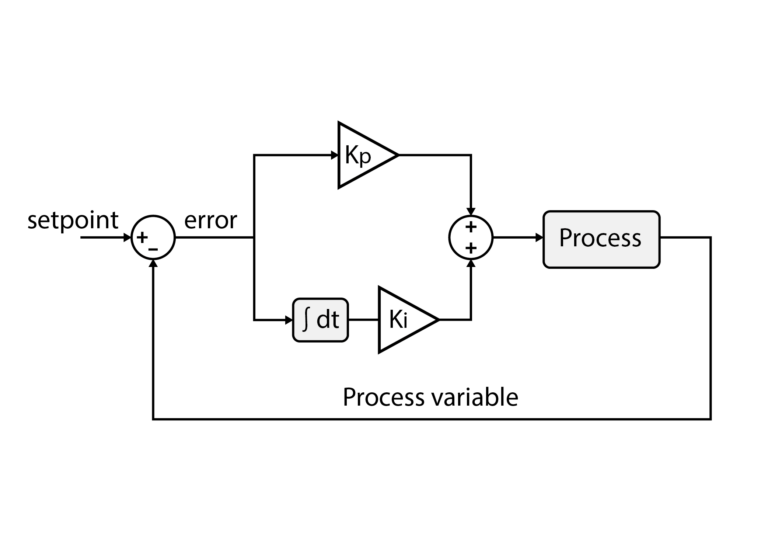
This technical note addresses possible implementations for a discrete PI controller and provides general insight into PI tuning strategies. It also includes practical implementations for…
Real time communication is essential in order to enable converter controllers to coordinate with other devices. B-Box RCP and other imperix controllers support several protocols…
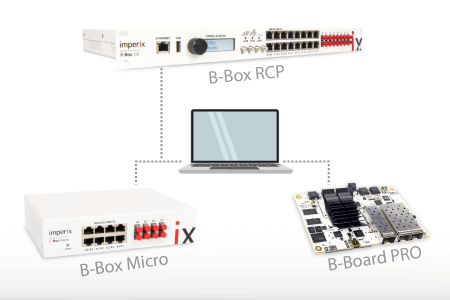
This page helps new users get started with imperix power electronic controllers. In particular, it explains how to deploy a user code onto these controllers,…
The DQ-type PLL is a basic Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) used to extract the phase information of three-phase voltages. It operates by minimizing the voltage projected…
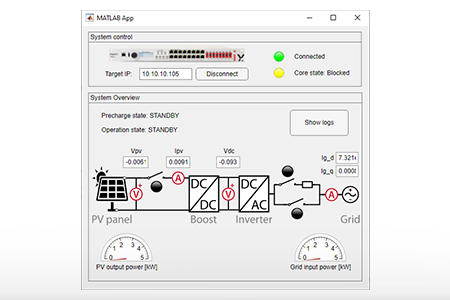
This note outlines the key considerations for developing a custom user interface specifically for the operation of Imperix power converters. Several possibilities are available to…
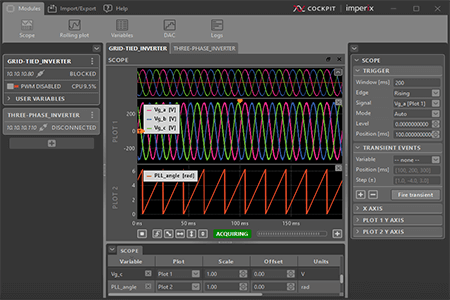
This user guide explains how to use imperix Cockpit to interact with imperix power converter controllers, namely the B-Box 4, B-Box RCP, B-Board PRO, the Programmable…

The User fault block is used to stop the converter operation from the user model. It makes the controller enters the FAULT state (user fault)…

This block writes a user-defined message in the log module of Cockpit. Numerical values can be inserted into the message using the conversion specifier “%f“,…
End of content
End of content