Table of Contents
This page provides the source files, namely the imperix firmware IP and project template creation script, to start programming the FPGA on imperix devices. After a description of the archives content, step-by-step procedures explain how to generate a working Vivado project from the source files or from project-specific scripts provided in the Knowledge Base, and how to update the firmware for existing sandbox projects.
To learn how to use the imperix IP, please refer to the getting started with FPGA page and the imperix IP user guide page.
To find all FPGA-related notes, you can visit FPGA development homepage.
Downloads
| Compatible SDK versions | Gen 4 (B-Box 4) | Gen 3 (B-Box RCP 3.0,B-Box Micro, B-Board PRO, TPI8032) |
| 2026.1 | 4.0 Rev. 0 FPGA_Sandbox_template_4.0rev0.zip | 3.10 Rev. 3 FPGA_Sandbox_template_3.10rev3.zip |
| 2026.1 2025.2 2025.1 | Not applicable. | 3.10 Rev. 1 FPGA_Sandbox_template_3.10rev1.zip |
| 2026.1 2025.2 2025.1 2024.3 | Not applicable. | 3.10 Rev. 0 FPGA_Sandbox_template_3.10rev0.zip |
Change logs
New in 3.10 Rev. 0
- Repurposing the SFP ports
One or multiple SPF ports can now be detached from RealSync and the corresponding GTX transceivers accessed via additional ports on the imperix firmware IP. The SFP ports can therefore be used for custom communication, using Aurora 8B10B for instance. - Saving of FPGA resource
Unused modulators can bow be disabled in the imperix firmware IP, significantly reducing the resource consumption of the IP in the FPGA. Users with large custom FPGA designs might take advantage of it to extend their design even further.
New in 3.10 Rev. 1
- Improved configurability of the RES block
The resolution and excitation frequency of the resolver can now be changed. The default values are 12-bit and 10 kHz, as set in the previous firmware versions.
New in 3.10 Rev. 2
Internal version.
New in 3.10 Rev. 3
- Support for remote debugging over the network
Thanks to the support of Xilinx Virtual Cable (XVC), it is now possible to instantiate and connect to on-chip Integrated Logic Analyzer (ILA) cores via Ethernet. This provides access to the internal FPGA signals without any physical JTAG cable, greatly facilitating the debug of FPGA logic. - Propagation of Ethernet between devices at full gigabit speed
An upgrade of the Ethernet-over-RealSync protocol – from Mbps to Gbps – allows inter-device traffic to reach the Gigabit speed in master-slave and multi-master setups.
Archives content
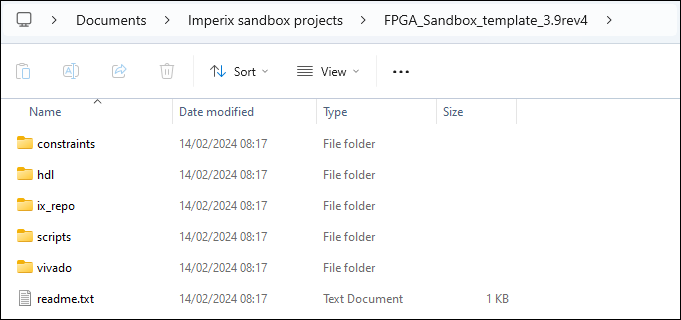
Content structure
The content of the archives follows the following structure.
| /constraints/ | Constraints associated to the imperix firmware, mainly assignation of top-level ports to physical package pins. |
| /hdl/ | Ready-to-use VHDL helper modules, detailed in the next section, provided by imperix for convenience. |
| /ix_repo/ | imperix firmware under the form of an IP and related interfaces |
| /scripts/ | Generation scripts to automatically create, open and configure a ready-to-use Vivado project, simplifying the initial setup. |
| /vivado/ | Location of the projects created via the generation scripts from /scripts/. |
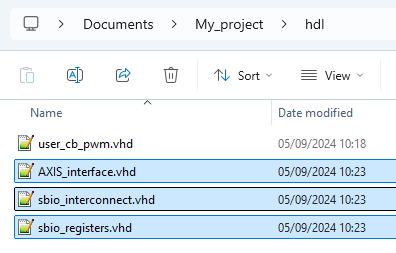
VHDL helper modules
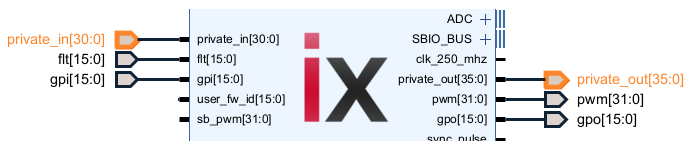
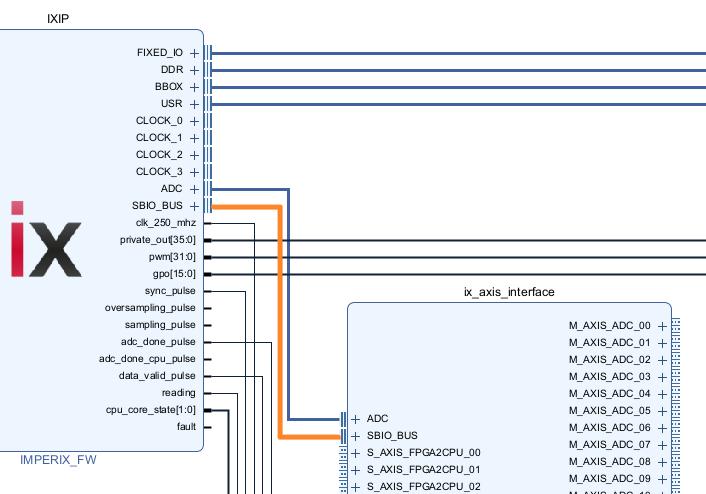
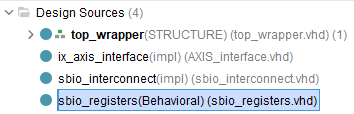
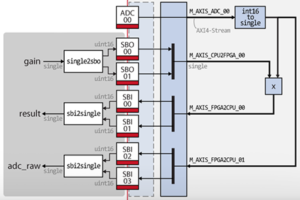
| AXIS_interface.vhd | Connects to the SBIO bus and ADC interface of the imperix firmware IP and provides the same access through AXI4-Stream interfaces. |
| AXIS_64_interface.vhd | Same module as the AXIS_interface.vhd, extended to 64 CPU2FPGA (SBO) and FPGA2CPU (SBI) registers. |
| AXIS_to_reg.vhd | Exposes AXI4-Stream input data through a simple, interface-free register, updating its value whenever the input data is valid. |
| resets.vhd | Generates reset pulses based on the firmware synchronization pulse and CPU state. |
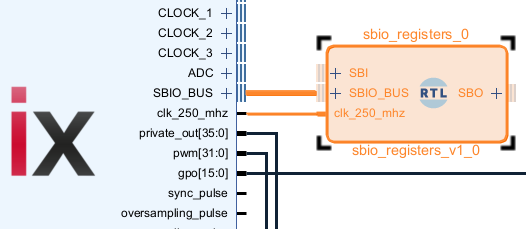
| sbio_registers.vhd | Connects to the SBIO bus interface of the imperix firmware IP, instantiates the SBIO registers and exposes them as ports for an easy access from the user logic. Works as a serial-to-parallel converter for the SBIO bus interface. |
| sbio_256_registers.vhd | Same module as the sbio_registers.vhd, extended to 256 CPU2FPGA (SBO) and FPGA2CPU (SBI) registers. |
| sbio_interconnect.vhd | Connects to the SBIO bus interface of the imperix firmware IP and splits the 1024-addresses range into four smaller 256-addresses ranges. |
| user_cb_pwm.vhd | Simple carrier-based modulator that basically takes a duty-cycle as input and produces the corresponding PWM outputs. |
Creating a new project
The creation of a new project can be achieved either manually, or through the provided generation scripts. Please refer to the desired creation procedure in the two following subsections.
Step-by-step project creation
To create the template manually, please extend the box below and follow the detailed procedure.
Project creation using the generation scripts
To automatically generate the template project via the provided generation scripts, please follow the detailed procedure below.
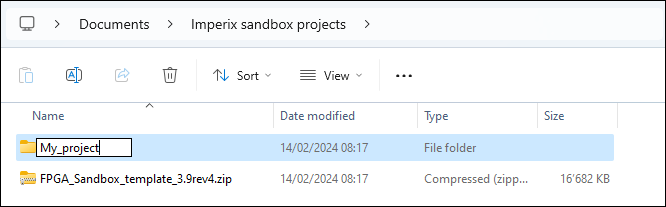
- Download the sources files FPGA_Sandbox_template_*.zip archive.
- Unzip it and save the content somewhere on the PC.
- Rename the folder to something more explicit.
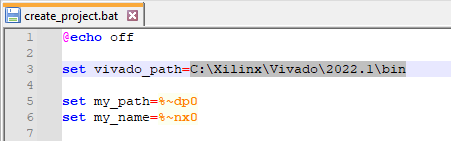
- Open scripts/create_project.bat using a text editor.
- Set the vivado_path variable to match the Vivado version installed on the PC.
- Double click on scripts/create_project.bat. Windows Defender SmartScreen may display a warning pop-up. Simply click More info then Run anyway.
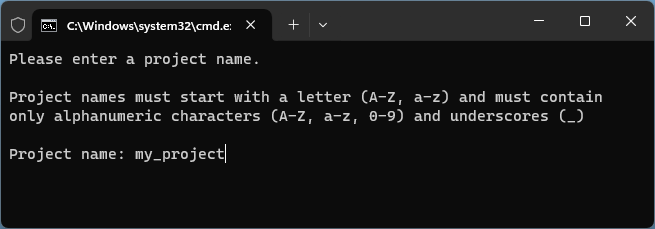
- Enter a project name and click Enter.
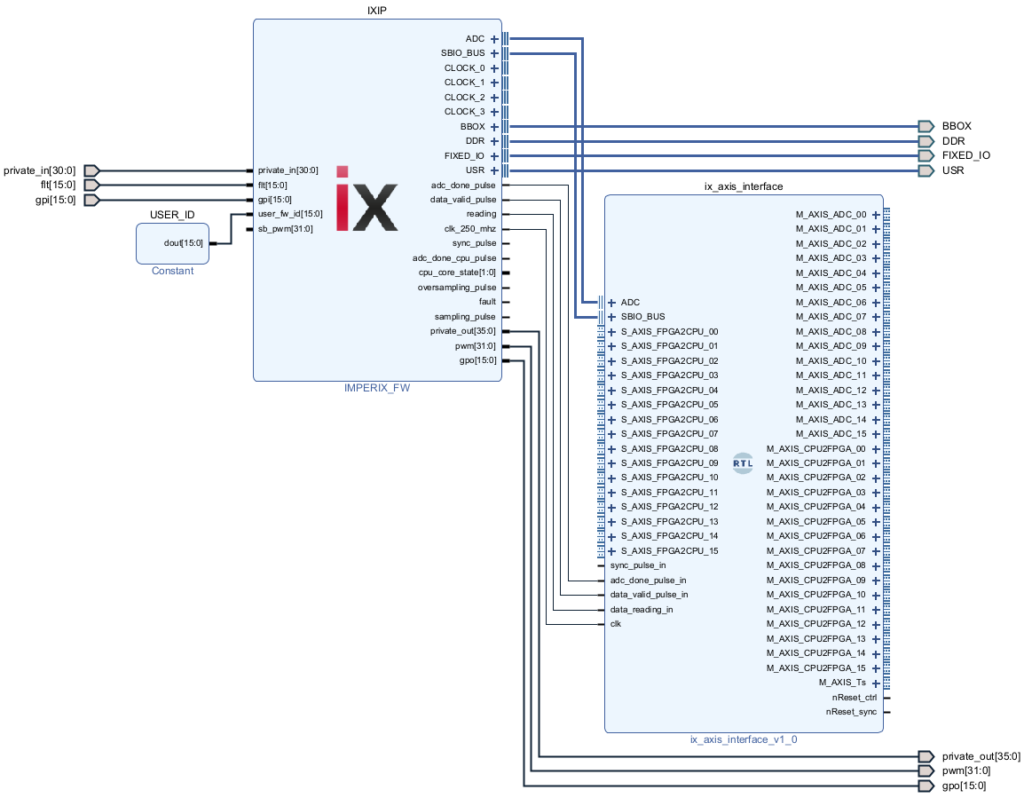
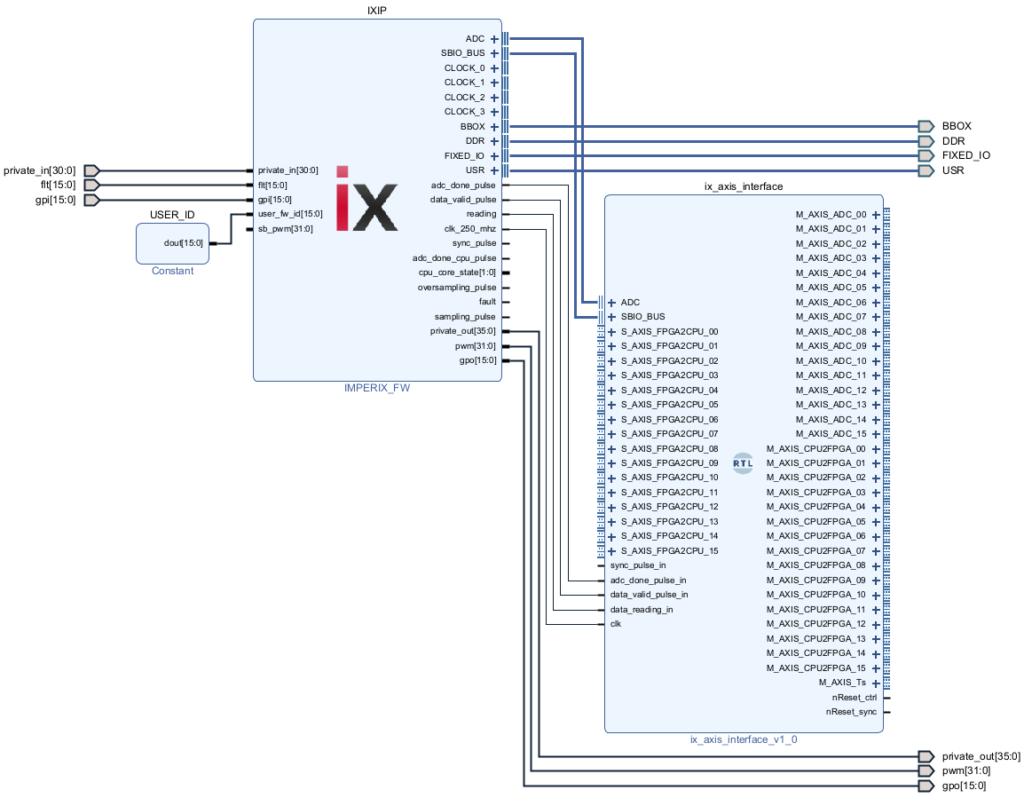
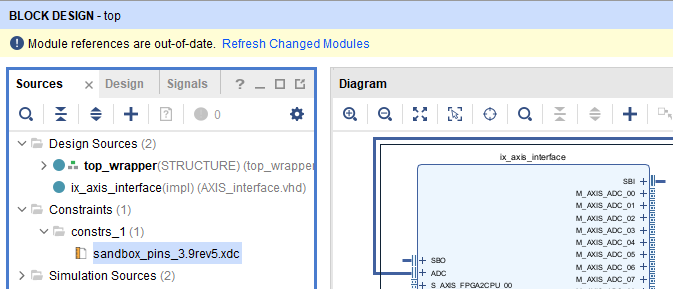
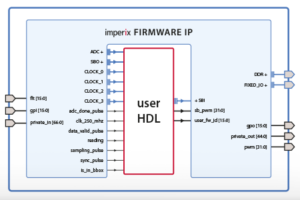
The Vivado sandbox project will be created and configured, its block design is shown below.
Starting from generation scripts
This section describes how to proceed when starting with a project-specific script downloaded on our Knowledge Base.
- Download the source files FPGA_Sandbox_template_*.zip archive.
- Unzip it and save the content somewhere on the PC.
- Rename the folder to something more explicit.
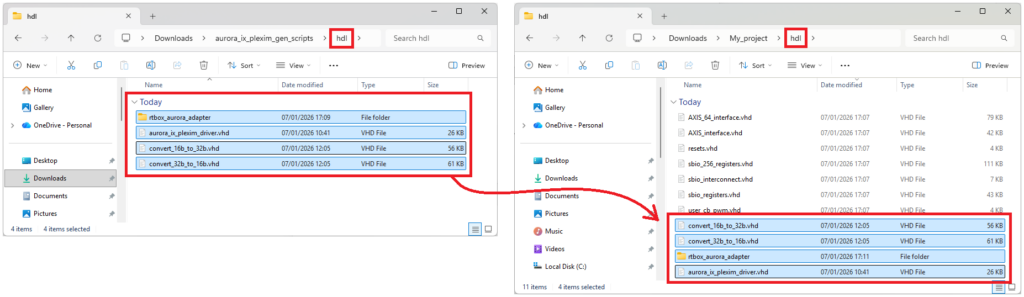
- Download the project-specific generation scripts on the page of interest in the Knowledge Base (e.g., aurora_ix_plexim_gen_scripts.zip in Aurora link with Plexim via SFP).
- Unzip it and open it.
- Copy-paste the content of each subfolder into the corresponding subfolder of the source files (e.g., content of <scripts folder>/hdl/ into <source files>/hdl/, etc.). If any, the scripts in the top-level of the scripts folder must be placed in <source files>/scripts/.
- Double-click on the newly copied <source files>/scripts/<script_name>.bat file. Windows Defender SmartScreen may display a warning pop-up. Simply click More info then Run anyway.
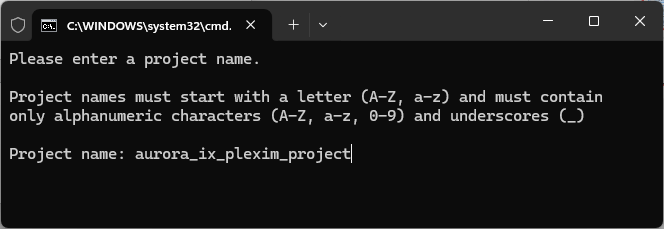
- Enter a project name and click Enter.
- Once the Vivado is created, click on Generate Bitstream. Vivado will proceed to the synthesis and implementation of the bitstream.
- Once generated, click on File > Export > Export Bitstream File and store the bitstream somewhere on the PC.
- Load the bitstream on the target with Cockpit.
- The FPGA is now ready to go.
- Next steps are generally to connect the physical setup, and download, build and load the Simulink (or PLECS) model for the CPU.
Upgrade procedure
This section describes how to upgrade the imperix IP from an existing Vivado project.
- Download the FPGA_Sandbox_template zip file for the targeted SDK version and unzip it.
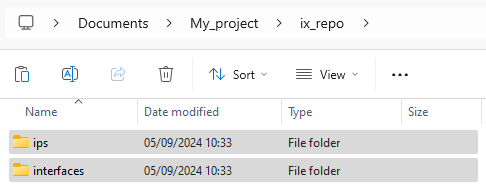
- In the <project_dir>/ix_repo/ directory, replaces the interfaces and ips folders with the ones from the freshly downloaded sandbox template.
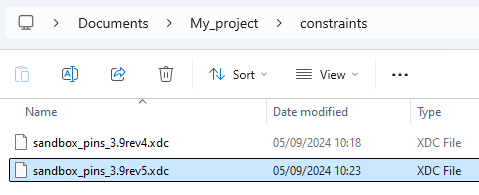
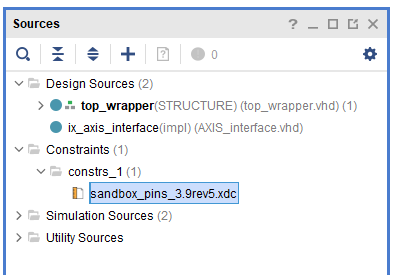
- Copy the new constraint file to <project_dir>/constraints/.
⚠️If modifications were made to the constraint file (e.g. to use USR pins), these modifications need to be reported to the new constraint file.
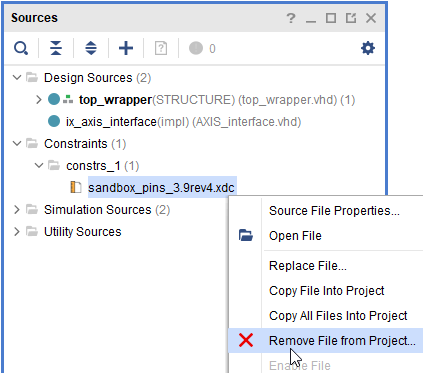
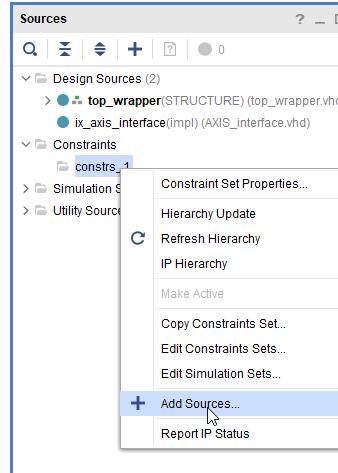
- Open the Vivado project. Remove the old constraint file and add the new one.
- Upgrade the imperix sandbox IP. It may generate warnings, which is expected.
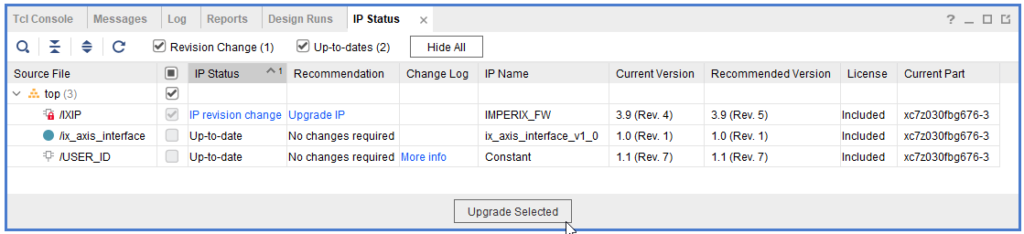
- Follow the expandable sections in the accordion below depending on the used imperix IP version.
Legacy IPs for older SDKs
| C++ or ACG SDK | imperix IP version | Minimal Vivado version required | Download |
| 2024.2 | 3.9 Rev. 5 | 2022.1 | FPGA_Sandbox_template_3.9rev5.zip |
| 2024.1 | 3.9 Rev. 4 | 2022.1 | FPGA_Sandbox_template_3.9rev4.zip |
| internal only | 3.9 Rev. 1 to 3 | 2022.1 | internal only |
| 3.8.x.x | 3.8 Rev. 1 | 2022.1 | sandbox_sources_3.8.zip |
| 3.7.x.x | 3.7 Rev. 1 | 2021.1 | sandbox_sources_3.7.zip |
| 3.6.x.x | 3.6 Rev. 1 | 2019.2 | sandbox_sources_3.6.zip |
| 3.5.x.x 3.4.x.x | 3.4 Rev. 1 | 2019.2 | sandbox_sources_3.4.zip |