Table of Contents
This technical note shows how an SPI communication link can be established between an FPGA and an external Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC). The development setup will consist of an imperix B-Board PRO evaluation kit and an LTC2314 demonstration circuit. The LTC2314 ADC driver will be developed using VHDL integrated into the user-programmable area (the sandbox) of the FPGA thanks to the FPGA customization feature of the imperix controllers. Three of the 36 user-configurable 3.3V I/Os of the B-Board will be used for the SPI communication with the ADC.
This note provides a VHDL implementation of the FPGA ADC driver. However, automated HDL code generation tools such as MATLAB HDL Coder or Xilinx System Generator can be used to create FPGA peripherals as shown on the custom FPGA PWM page.
Related notes
Information on how to set up the toolchain for the FPGA programming is available on the Vivado Design Suite installation page.
Quick-start information on how to use the sandbox is provided on the getting started with FPGA page.
Software resources
The FPGA ADC driver resources can be downloaded by clicking on the button below. It contains the VHDL driver LT2314_driver.vhd, its associated testbench LT2314_tb.vhd, as well as the C++ drivers implemented using the C++ SDK.
FPGA ADC implementation
This example implements a full-custom FPGA ADC SPI driver for the LTC2314-14 serial sampling ADC with the following settings:
- It uses the LTC2314 SCK continuous mode (see next figure)
- The SCK frequency is configurable using a postscaler (
postscaler_in) - The conversion is started upon the assertion of
sampling_pulse
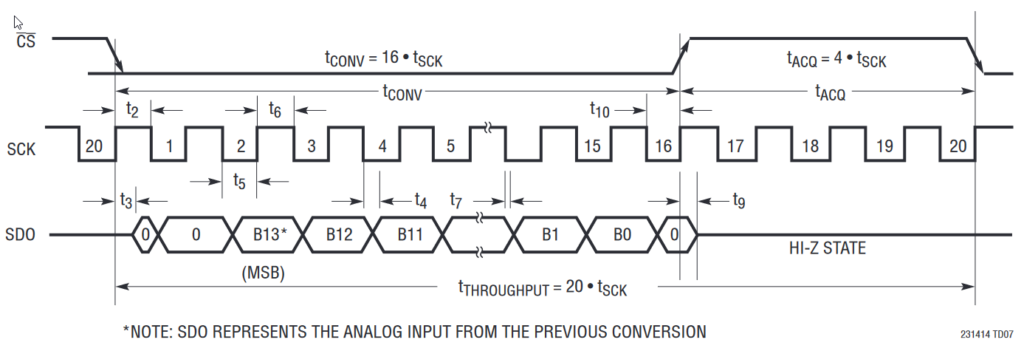
FPGA ADC testbench
A VHDL testbench modeling the LTC2314 behavior has been written in order to validate the FPGA ADC driver behavior.
Deployment on the B-Board PRO FPGA
To learn how to add a VHDL module into B-Board FPGA firmware using Xilinx Vivado, please read the getting started with FPGA page. The ADC SPI driver has interfaced as follow:
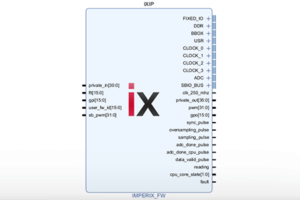
spi_sckis connected to the physical pinUSR[0]spi_cs_nis connected to the physical pinUSR[1]spi_dinis connected to the physical pinUSR[2]postscaler_inis connected toSBO_reg_00(configuration register)data_outis connected toSBI_reg_00(real-time register)
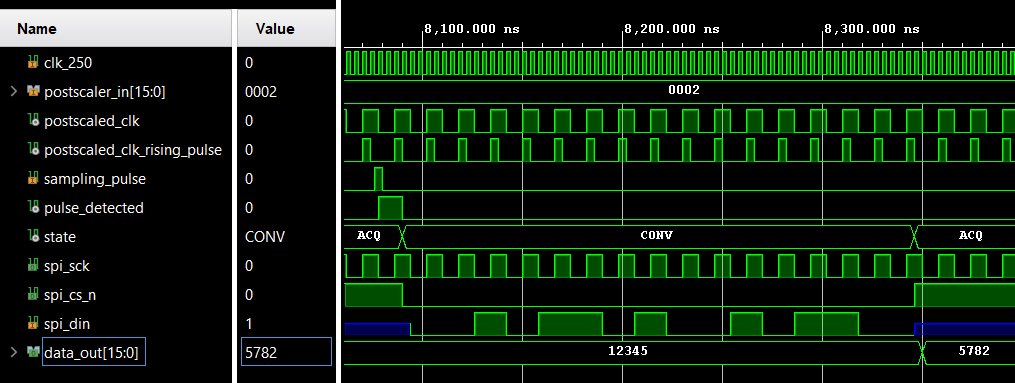
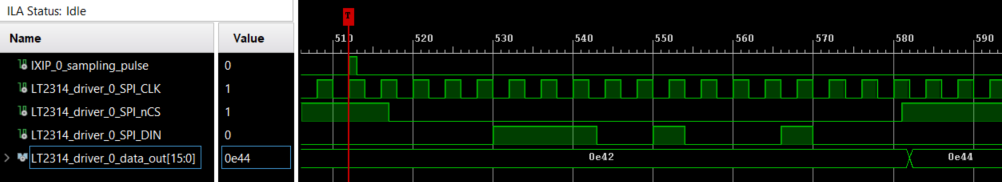
Furthermore, the signals spi_sck, spi_cs_n, spi_din, data_out and sampling_pulse are also connected to an Integrated Logic Analyzer (ILA), allowing them to be observed during run-time.
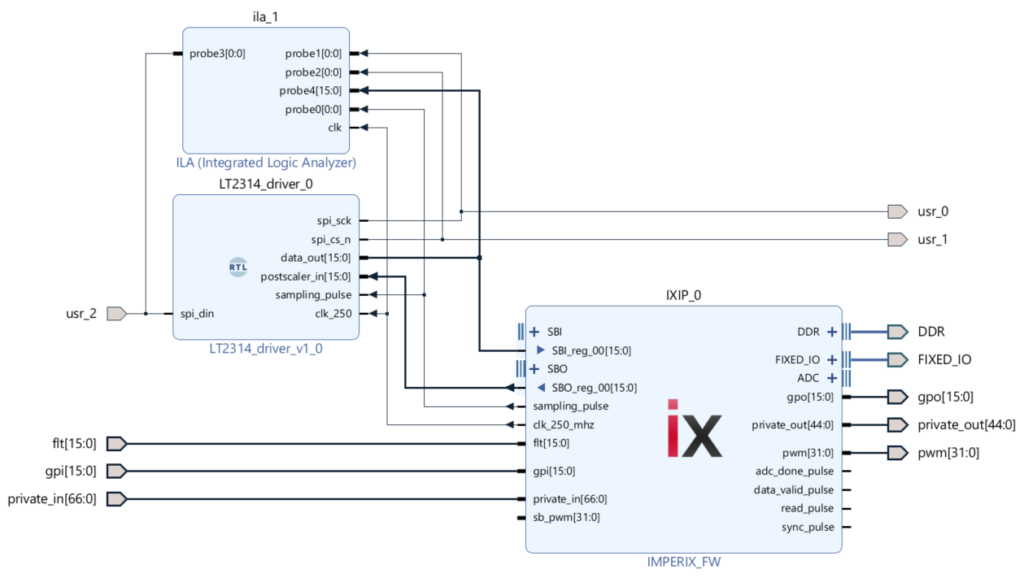
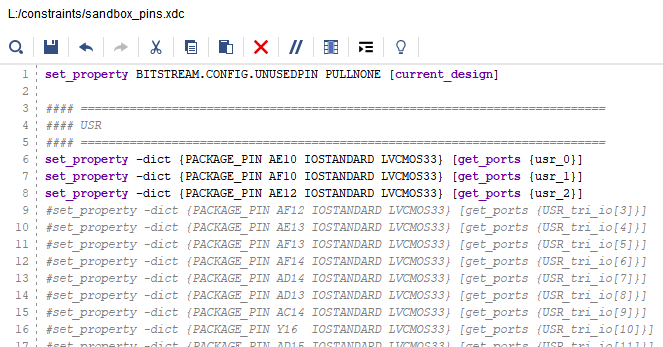
Using the imperix 3.3V USR pins
The SPI signals (SCK, nCS, and MISO) of the ADC driver are connected to 3 of the 36 user-configurable 3.3V I/Os of the B-Board (usr_0, usr_1, and usr_2). The physical pin constraint file sandbox_pins.xdc file must be edited by the user to match the external port names.
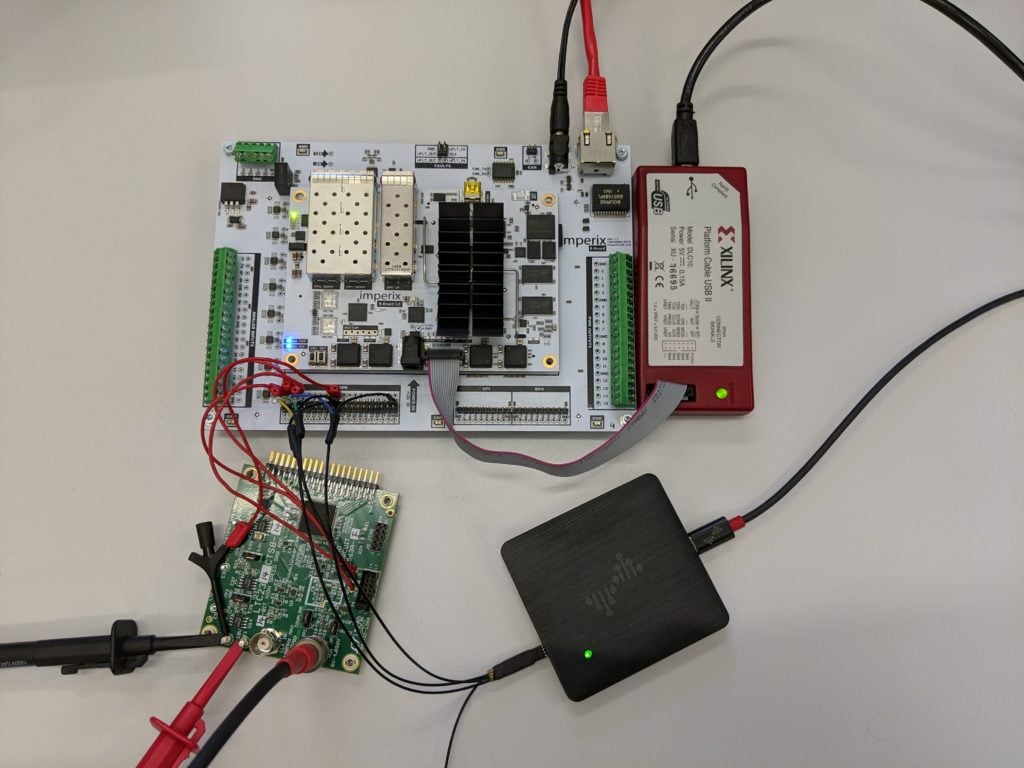
Experimental results
The following hardware was used:
- B-Board evaluation kit
- LTC2314 demonstration circuit
- Xilinx JTAG Platform Cable USB II
- DSLogic Plus logic analyzer
The following C++ code has been used to test the LT2314 driver.
define ADC_GAIN (4.096/8192.0)
int adc_raw;
float Vmeas;
tUserSafe UserInit(void)
{
Clock_SetFrequency(CLOCK_0, 20e3);
ConfigureMainInterrupt(UserInterrupt, CLOCK_0, 0.5);
Sbi_ConfigureAsRealTime(0); // SBI_reg_00 contains the ADC value (LT2314_driver data_out)
Sbo_WriteDirectly(0, 2); // SBO_reg_00 is the clk postscaler (LT2314_driver postscaler_in)
// postscaler = 2 -> SCK = 62.5 MHz
return SAFE;
}
tUserSafe UserInterrupt(void)
{
adc_raw = Sbi_Read(0); // read SBI_reg_00
Vmeas = adc_raw * ADC_GAIN; // convert to Volts
return SAFE;
}Code language: C++ (cpp)The external SPI signals can be observed using a physical logic analyzer such as the DSLogic Plus:
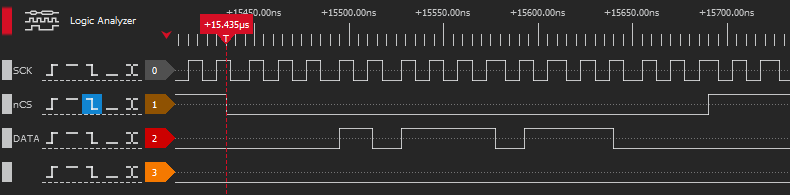
Secondly, the Xilinx Integrated Logic Analyzer (ILA) allows to observe internal signals too:
Finally, the end result can be plotted in the Cockpit monitoring software, attesting that the SPI module works correctly.